Top 10 UX Research Methods You Need to Know

Discover key methods like qualitative, quantitative, generative, and evaluative research. Discover the benefits of each and how to apply them for user-centered designs.
Key Takeaways
- UX research methods bridge user needs and product functionality, emphasizing qualitative and quantitative approaches to gather actionable insights.
- Generative research focuses on uncovering user needs and exploration of ideas in early product development, while evaluative research measures usability and effectiveness in later stages.
- Continuous user research integrates ongoing feedback into product development, enhancing user satisfaction and adaptability to changing market conditions.
Overview of UX Research Methods
Understanding user needs and behaviors is critical to creating products that resonate with users. UX research methods serve as the bridge between user needs and product functionality, ensuring that designs are aesthetically pleasing but also practical and enjoyable to use. The first step in any successful product development process is selecting the right UX research method, tailored to the specific stage of development and the goals at hand.
UX research methods can be broadly categorized into qualitative, quantitative, generative, evaluative, attitudinal, and behavioral. Each category offers unique insights that inform different aspects of the design process. For example, qualitative methods like user interviews provide in-depth insights into user experiences and motivations, while quantitative methods such as surveys offer statistical data on user behaviors and preferences.
Selecting the appropriate method requires a clear understanding of the problem being addressed and the research goals. This ensures the data collected is relevant and actionable, empowering teams to make informed design decisions. Integrating user research at every stage helps teams design products that meet user needs and expectations.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
Qualitative and quantitative research are the two main pillars of UX research methods. Each serves a distinct purpose and provides different types of insights. Qualitative research aims to capture subjective insights into users’ experiences. It delves into their motivations and emotions in detail. This type of research often answers the “why” behind user behaviors, allowing researchers to delve deeper into users’ thoughts and feelings.
On the other hand, quantitative research emphasizes numerical data to answer questions related to “what,” “where,” and “when.” It involves collecting statistical quantitative data that can be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and correlations in user behavior. Quantitative methods provide broad insights essential for data-driven decisions.
Combining qualitative and quantitative research methods can yield better insights, providing a holistic view of user behavior. This approach allows researchers to validate findings from one method with the other, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of user needs and preferences. Let’s dive deeper into the specific types of qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Types of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research methods are invaluable for uncovering the nuanced motivations behind user behaviors. One of the most common qualitative methods is user interviews. These interviews provide an opportunity to gather in-depth insights about users’ experiences, needs, and motivations through dynamic discussions and observation of verbal and non-verbal cues. Direct engagement with users helps researchers gather rich qualitative data that other methods might miss, including user research methods.
Focus groups are another popular qualitative research method. They involve 5-10 participants discussing their experiences and opinions about a product or service. Focus groups can be conducted at various stages of product development, offering diverse perspectives and the ability to explore user preferences flexibly. This method is useful for generating ideas and understanding user attitudes in a collaborative setting.
Diary studies are a longitudinal qualitative research method where users self-report their activities, thoughts, and feelings over a period of time. This approach provides rich qualitative insights about user behaviors across different contexts, illustrating how products fit into their daily lives. Diary studies capture organic feedback on repetitive or unpredictable activities, helping researchers understand long-term user experiences and identify patterns.
Types of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research methods are essential for collecting broad, statistical data on user behaviors and preferences. Surveys are one of the most prevalent quantitative methods. They can reveal user attitudes and behaviors through statistical analysis, providing broad insights into user opinions and trends. While surveys are effective for gathering large amounts of data, they may lack the in-depth insights and context that qualitative methods provide.
A/B testing is another important quantitative research method. This process involves randomly dividing users into groups to test different versions of a product and ascertain which performs better based on user interactions. Metrics such as click-through rates and actual purchases are key measurements in A/B testing, providing direct, evidence-backed feedback on design choices.
Behavioral analytics is a powerful tool for tracking user interactions and deriving insights about conversion rates, user engagement, and other key metrics. By analyzing behavioral data on bounce rates, time on task, and other behaviors, researchers can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance the user experience. These quantitative methods are crucial for validating design decisions and ensuring products meet user expectations.
Generative vs. Evaluative Research
Generative and evaluative research are two fundamental types of UX research methods, each serving a distinct purpose in the design process. Generative research aims to uncover new ideas and insights for the design process, typically conducted at the start of product development. This type of research helps identify user needs, behaviors, and pain points, providing a foundation for creating innovative solutions.
Evaluative research, on the other hand, measures how effectively a product fulfills user needs and provides insights for improving existing designs. This type of research is crucial for validating if the design successfully addresses the problems identified earlier in the product lifecycle. Evaluative methods allow researchers to pinpoint usability issues and make necessary adjustments to improve the user experience.
Choosing between generative and evaluative research depends on the phase of the product development process. Early stages favor generative methods to explore new ideas, while later stages lean towards evaluative techniques to refine and validate designs. Let’s explore specific methods for each type of research.
Generative Research Methods
Generative research methods play a crucial role in identifying new opportunities and understanding user needs, which is essential for developing effective design solutions. Stakeholder interviews and field studies are common generative research methods. Stakeholder interviews involve engaging with key stakeholders to gather insights about their expectations and requirements, ensuring the design aligns with business goals.
Field studies allow researchers to observe users in their natural environment, uncovering external factors that influence user experience. This method provides a holistic understanding of user behaviors and contexts, which can inform the design process. For example, Airbnb used generative research to identify a need for improved check-in processes, leading to the development of a global check-in tool.
Concept testing is another generative research method that gauges audience interest and feasibility for new products before commitment. By using methods like surveys and interviews, researchers can validate ideas and ensure they resonate with users. These generative methods help teams create user-centric products that address real user needs and pain points.
Evaluative Research Methods
Evaluative research methods are essential for assessing the effectiveness of design solutions and identifying areas for improvement. Usability testing is one of the most common evaluative methods. It involves observing users as they complete tasks to identify usability issues and gather feedback. Outputs of usability testing include detailed reports on usability issues and session recordings, which provide valuable insights for refining designs.
Tree testing is another evaluative method used to evaluate the findability and navigational performance of information in a product’s hierarchy. This method is ideally conducted early during the design or redesign process and focuses on the navigation structure rather than visual design. By testing the effectiveness of the information architecture, tree testing helps ensure users can easily find what they need.
Click tracking allows researchers to monitor where users click on websites, providing insights into user navigation patterns and identifying usability issues. First click testing, a form of click tracking, evaluates the intuitiveness of a design by assessing which element users click on first.
Evaluative research methods help teams create user-friendly designs by identifying and addressing usability issues through a user research method.
Attitudinal vs. Behavioral Research
Attitudinal and behavioral research are complementary approaches to understanding user needs and behaviors. Attitudinal research focuses on understanding users’ beliefs, opinions, and motivations. It collects insights about users’ thoughts and feelings through direct feedback methods like surveys and interviews. This type of research provides context and understanding of user feelings and perceptions, helping to identify user motivations and preferences.
Behavioral research, on the other hand, gathers unbiased data by observing actual user interactions with a product. It focuses on what users do, rather than what they say, providing a more accurate picture of user behaviors. Behavioral research reveals actual user engagement with a product, highlighting areas for improvement.
Combining both attitudinal and behavioral research can enhance the understanding of user behavior by correlating what users claim with their actual actions. This comprehensive approach ensures that researchers capture both the “why” and the “what” of user behavior, leading to more informed design decisions.
Remote vs. In-Person Research
The choice between remote and in-person research methods depends on the specific needs of the project and participant demographics. Remote research offers several advantages, such as cost-effectiveness and the ability to access a wide and diverse participant group. It eliminates travel and associated logistics, making it a more convenient option for researchers and participants. Additionally, remote testing offers greater scheduling flexibility, which can reduce participant dropout rates.
In-person research, however, provides richer contextual insights by allowing researchers to observe participant behaviors in their natural environments. This method fosters stronger participant engagement through direct interaction, which can yield more honest and detailed feedback. In-person sessions can be particularly valuable for capturing non-verbal cues and understanding the context of user interactions.
Technical difficulties, such as poor internet connections, can hinder the effectiveness of remote research. In contrast, in-person sessions can be logistically challenging due to the time and cost requirements for travel and venue arrangements. Choosing between remote and in-person research depends on project goals, participant availability, and budget constraints.
Moderated vs. Unmoderated Research
Another key decision in UX research is choosing between moderated and unmoderated research methods. Moderated testing involves real-time interaction with a facilitator, who guides participants through tasks and captures spontaneous insights through direct questioning and observation. This method provides deeper qualitative insights and is particularly useful early in the design process for gathering feedback on concepts and prototypes.
Unmoderated testing, on the other hand, allows users to complete tasks independently, often using online tools. This approach is faster and cheaper to implement, making it effective for gathering large quantities of data quickly, especially at later stages of the design process. Unmoderated tests enable access to a broader participant pool and can be completed in participants’ environments, adding a layer of naturalistic validity to the findings.
The choice between moderated and unmoderated methods depends on factors like budget, timeline, and the stage of the design process. While moderated research offers rich qualitative data, unmoderated research provides the efficiency and scalability needed for rapid iteration and validation.
Continuous User Research
Continuous user research shifts from a one-time phase to an ongoing process integrated into product development. This approach helps teams rapidly adapt to changing user preferences and market conditions, fostering a user-centric culture by consistently integrating user insights into the design process. Real-time user feedback is essential for iterative improvements throughout the product lifecycle, ensuring products remain relevant and effective.
Establishing strong feedback channels is crucial for gathering ongoing user insights. Utilizing tools like session recordings and heatmaps allows for continuous data analysis of user interactions, helping teams identify areas for improvement and track the impact of design changes. For example, Google for Education rapidly adapted Google Meet by incorporating feedback from teachers, adding essential features to enhance the user experience for online classes.
Embracing continuous user research enables organizations to create user-centric products that evolve with users’ needs and preferences. This ongoing process not only improves user satisfaction but also reduces the risk of product failure by ensuring that user feedback informs every design decision.
Choosing the Right UX Research Method
Selecting the right UX research method begins with clearly defined research questions and goals. Factors such as the project stage, research goals, participant availability, and budget constraints play a crucial role in determining the most appropriate method. Different stages of product development require different research methods tailored to the specific problems being addressed. For instance, generative methods are ideal for the early stages of exploring new ideas, while evaluative methods are better suited for later stages to validate and refine designs.
Budget and available resources significantly affect the choice of UX research methods that can be realistically implemented. Frameworks can help streamline the decision-making process by providing structured approaches to selecting appropriate methods based on various constraints.
Adapting these frameworks to the specific needs of your organization can enhance the effectiveness of the chosen research methods. Ultimately, the goal is to select the right UX research method that aligns with your project’s objectives and constraints, ensuring the data collected is relevant, actionable, and drives user-centric design decisions.
UX Research Examples
Real-world applications of UX research demonstrate its impact on product development and user satisfaction.
Fundid
One such example is the Fundid, where Netguru conducted user research to understand women’s attitudes toward finances and business banking. The final report included user personas, an early adopter profile, and valuable insights thatguided Fundid’s approach to banking services. These findings helped define the scope of their MVP and the general direction of their product roadmap.

Virtual Try-On
Another case study involves Netguru’s internal UX research for virtual try-on solutions aimed at enhancing retail and e-commerce offerings. The primary goal was to gather insights for an industry report, identifying weaknesses in existing solutions and opportunities for improvement. This research deepened their understanding of the virtual try-on market and identified potential future opportunities.
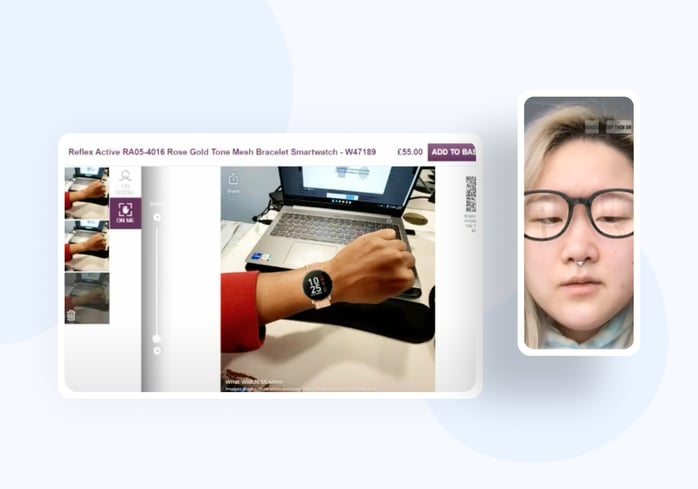
These case studies illustrate the vital role of UX research in tailoring products to meet user expectations and drive success. Applying various UX research methods enables organizations to gain insights that inform design decisions and create user-centric products.
Summary
In summary, UX research methods are essential for understanding user needs and ensuring that products are functional and enjoyable. From qualitative insights gathered through user interviews and focus groups to quantitative data obtained from surveys and A/B testing, each method provides unique benefits that contribute to a comprehensive understanding of user behavior. The choice between generative and evaluative research, as well as the decision to conduct research remotely or in person, depends on the specific goals, stage of development, and available resources.
By integrating user research into every stage of the design and development process, teams can create products that truly resonate with users. Continuous user research further enhances this approach by allowing real-time feedback and iterative improvements, ensuring products evolve with changing user needs. The case studies of Fundid and Netguru’s virtual try-on solutions demonstrate the tangible benefits of applying the right UX research methods.
Ultimately, selecting the right UX research methods empowers teams to make informed design decisions, leading to user-centric products that stand out in the competitive market. Embrace the power of UX research to create products that not only meet but exceed user expectations.






