5+ Benefits of Product Design Sprint to Your Business and Your Digital Product (UPDATED)

In fact, starting and running a company is a constant struggle to win new clients, increase awareness, respond to customer needs and successfully launch products to the market. These challenges often raise questions on how it should be done properly.
Having tested numerous solutions we’ve adopted Product Design Sprint, a tool initially developed within Google, which will give you answers to these strategic questions. Our clients confirm its effectiveness and enumerate its many benefits. We picked some universal advantages of PDS to give you an idea how your business can profit from adopting this framework.
What is a Product Design Sprint?
A good product idea and execution aren’t enough in today’s world. To succeed, you’ll need to answer critical business questions business strategy, research, design thinking, effective collaboration, innovation, prototyping, and testing – all this with a user-centered approach in mind.
That’s why we introduced Product Design Sprints, a series of workshops based on Google Ventures’ design sprints. They have been popularized thanks to Jake Knapp’s bestselling book “Sprint”, in which you can read more about the methodology, its practical applications, and real-life examples from the business world.
A Product Design Sprint is a five-step (ideally 5-day) workshop that helps brands launch better digital products. Through quick idea validation, fast prototyping, and testing, you can minimise the risk of a failure. It can help you solve complex challenges with a fraction of the resources.
Who can benefit from a Product Design Sprint?
A Product Design Sprint is a perfect idea not only for clients who already have some experience with various kinds of design services for their products. Our workshops differ from each other depending on the problem our clients are facing at the moment. We always meet in advance to get a better understanding of whether they:
- have a rough idea for a product or a problem to solve;
- have a product and want to identify pain points to enhance it;
- have a product and want to invest in new, more complex features.
Each and every case is different, and so we always analyse it separately based on research prepared before the workshop. It’s crucial that we have a lot of data and materials to study before the actual workshop so we can understand the problem better.
We prepare our workshops individually for each project and adjust the exercises so that our ‘sprint’ can give as much value as possible to our clients. Sometimes, it means putting more emphasis on the product's Value Proposition, because the client wants so many features that we think they lost focus on the core purpose of the product. In other cases, we focus on specific features or analyse current user journeys to spot any pain points and work together on finding solutions.
![Edit Page | [S][N] Product Design Sprint - Narrative (Natalia) 2019-02-26 16-25-30](https://www.netguru.com/hs-fs/hubfs/Edit%20Page%20%7C%20%5BS%5D%5BN%5D%20Product%20Design%20Sprint%20-%20Narrative%20(Natalia)%202019-02-26%2016-25-30.png?width=649&name=Edit%20Page%20%7C%20%5BS%5D%5BN%5D%20Product%20Design%20Sprint%20-%20Narrative%20(Natalia)%202019-02-26%2016-25-30.png)
What does the process look like?
A Design Sprint consists of five stages, often corresponding to five days. In a nutshell, the stages are as follows:
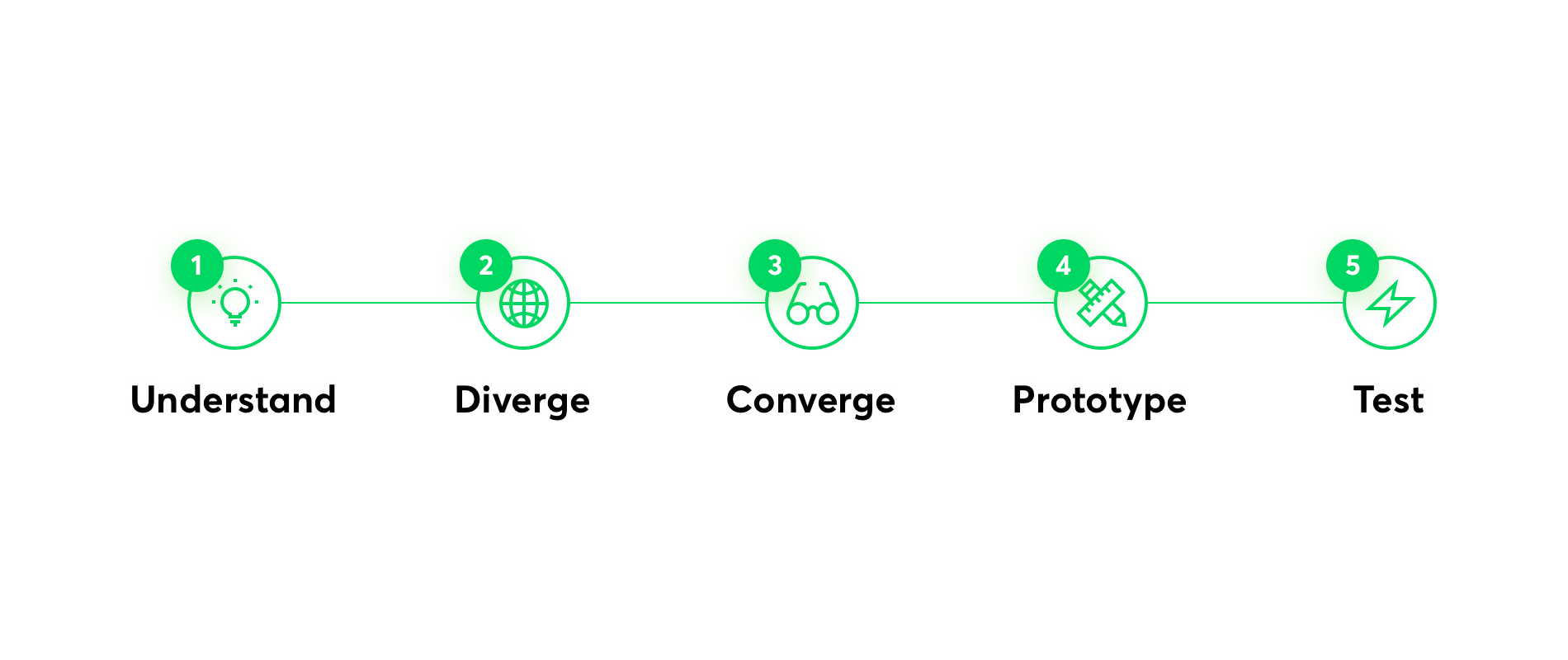
Day 1: Understand
The first day is all about getting insights about the users’ needs, business needs, and technology capacities. We methodically discover your business needs, user needs, and technology capacities. This allows us to decide on the main goal and to focus on it. Also, understanding technical challenges and risks lets us conceive a realistic estimation for product design and development.
Discussion during this stage is essential to create a roadmap for the sprint week. We run some exercises to paint a bigger picture of the problem. Benchmarking competition and creating personas is also an important part of this process. It entails deeper market research and is key for not only product design, but also for building the entire marketing strategy, including your go to market and future launch.
Having laid the foundations, we can concentrate on the important things, so we will be able to develop what is indeed necessary. At the end of the day, you pick the main goal you want to achieve during the sprint.
Day 2: Diverge
On the second day, we focus on generating and exploring as many ideas as possible. We’ll first review existing solutions, including their strong and weak points. The participants will also perform exercises to build new insights and solutions. Through brainstorming sessions and individual analyses, each team member will propose their ideas that will later be studied and tested.

Day 3: Converge
At this stage, we’ll have plenty of ideas which the team came up with during the previous two steps. The team’s goal now is to identify the best ideas and decide which of them should be prototyped in the next step. We’ll critique each solution in relation to the main goal. Based on the selected ideas, we’ll sketch a step-by-step roadmap, sitemap or a process map, which will be used for crafting a prototype.
Multiple ideations on one solution let you quickly analyse and reject irrelevant options, while avoiding misunderstandings and conflicts which often disturb efficient collaboration. Internal alignment is key to keeping the right direction! If you make your decisions together, you will stick to their execution together.
Day 4: Prototype
On the fourth day, it’s time to put all that the team developed into practice. You will turn your storyboard into a prototype – a realistic artifact you will then test with a customer. Now any potential pain points or major problems with the product can be easily detected.
The main assumption here is that you will only build the customer-facing surface of your product or service. In this way, the prototype will be up and running in just one day – ready for review in the final stage.
This stage will validate your solutions before you start spending your money on designing and developing an actual product, thus reducing the risk. If the test proves failure of the product - it will simply not be developed and you will not spend your time and money on something nobody wants. Or, you may go on and build it in the direction desired by the testers.
Day 5: Test
GV calls this phase the “moment of truth”. This is when you test the ideas with users, business stakeholders, and technical experts and hear direct feedback from them. This stage will validate your solutions before you start spending your money on designing and developing an actual product. At the end of the fifth day, you’ll have a clear idea of what you should do next.
We adjust the workshops to our clients’ needs. Sometimes, we even make them shorter to focus mainly on the first three phases.
Usually in such sprints we provide you with a Project Manager and a Product Designer who heads the workshop and acts as a mentor. We also ask our developers to attend if we feel like we need a reality check on our ideas.

Benefits of design sprints for your business
Product Design Sprint is a collaboration framework for answering critical business questions through design, prototyping and user research. The process includes a set of methods that are selected from some of the greatest practices of business strategy, design thinking, user research and even psychology. Furthermore, it helps to avoid miles of e-mail messages endless conversations and arrangements, which often lead to miscommunication between the parties involved. See what you can win thanks to PDS:
1. Simple solutions to complex business challenges
Right from the beginning, together with your stakeholders, your task is to set a goal and create an explicit vision for failure and success of this sprint. The main reason to conduct the sprint is to find all pain points and convert them into valuable solutions. Along with effective communication, it empowers contributors to share ideas, risks and doubts that can affect the final results. At the end you can gather all doubts, assumptions and verify them with clients. The collaborative approach enables you to get answers to complicated problems within a short period of time. It would be harder in a different environment.
2) Speed
Agility is especially interesting for large organisations whose tremendous growth has lead them to a corporate size and structure. Bureaucracy and slow processes are often seen as the inseparable part of scaling a business, so definitely speed is the main topic on the table.
“Speed is the new currency of business” Marc Benioff — CEO Salesforce; Davos 2016
The sprint itself is meant to be short and agile, as it is easily adapted to the complexity of a project. It speeds up new product discovery. For instance Spotify: despite being a large company, it is able to maintain agility by giving small focused teams the autonomy to explore an opportunity within a Product Design Sprint. They validated and prototyped their Spotify „Running” project in 5 days with their own adaptation of design sprint.
3) Smaller Risk
The process produces a prototype, or an MVP within just a couple of days. In this way, you can minimise risk by reducing time and budget on validating your ideas. Imagine that you can shrink months of development and feature testing into just a few days. It is a perfect method to create MVP in a blink of an eye. Remember, the faster you prototype, the faster you can validate your idea with investors, customers and other stakeholders. That gives you extra time for improvements or changes in case of failure. Huge companies like Google, P&G, AirBnB, or Spotify are using this PDS methodology to transform their companies and build competitive advantage, without huge failures along the way.
Moreover, the prototype can be transmitted directly to developers who will immediately know what to do and understand your vision, thus saving you months of work.
4) Efficient collaboration
Product Design Sprints foster collaboration with varied groups of people, with different skillsets. A multidisciplinary team works together and exchanges ideas, learning from each other. The team includes both domain knowledge holders and client-side-ideators - each voice is heard and considered equally important. More than just a project manager and product designer engage in the sprint (the latter leading the workshop) - we may also ask for the help of developers. This way a feasibility check is performed, where developers can immediately verify whether creative ideas are possible to be implemented.
It is an extremely satisfying experience, when you are able to spark creativity, encourage people to think outside the box and compare their perspectives from completely distinct fields. Such a group brainstorming session is way more effective than analysing the problem by individuals separately. You skip unnecessary arrangements, misunderstandings and loads of email correspondence. During the Sprint, there is no time for a lack of organisation and ineffective discussions. As a result, you save time, money and stress. On top of that, the variety of solutions that come up during workshops, can be surprising and let in a breeze of freshness.
5) Services validated by customers
Nowadays companies underestimate the value of the user-centered approach. This often leads to misunderstandings and missing market needs. From the PDS perspective, it is one of the most important pillars in this framework. That means that during the workshops members have to act with empathy and remain aware of the customer’s needs. What’s more, the integral part of this process is listening, trust and building meaningful relationships with users. This approach builds products from a user’s perspective and with the needs that they want to fulfill in mind. Did you know that thanks to Design Sprint, Airbnb developed itself from a small startup to one of the most popular services for renting accommodation?
How Product Design Sprint helps you launch a better product
Our clients confirm that they provide an actionable product roadmap for product development or a prevalidated prototype. But what are the main benefits of a design sprint if you want to release a new product to the market?
- Identifying key stakeholders. A broad perspective on the environment can help you identify all the stakeholders that have impact on your projects and whom your product will influence. You will be able to choose the key stakeholders who will help you move the project towards success.
- Users understanding. The workshops members have to act with empathy toward the customer’s needs. The sprint is based on is listening, trust, and building meaningful relationships with users. We run multiple exercises that will help you better understand user needs, pains, and behaviors and prioritize them.
- Lower risk. The sprint shrinks months of development and feature testing into just a few days. The faster you prototype, the faster you can validate your idea. Design sprints encourage effective communication, sharing ideas, and dispelling doubts. The approach enables getting answers to complicated problems.
- Fast prototyping. Idea validation is essential to succeed on the market and the best tool to achieve this it to create a prototype of your solution. The sprint itself is meant to be short and agile and it speeds up new product discovery. Therefore, your prototype will be ready for testing on the fifth day of the workshop.

Product Design Sprint as a tool to improve internal processes
Running a business is a constant fight to increase efficiency and to simplify complex processes. Challenges pop up every day and you struggle to solve them. If only you had a proven method that would help you successfully sort out the issues. With Product Design Sprint you can solve many problems. This flexible framework can be adjusted to a variety of challenges that appear within your company. Most frequently, the issues are related to services and people that deliver them - many of which can be solved with PDS.
Develop further vision for progress
It’s much clearer when your team have specified metrics, vision and goals. There are no guesses who is responsible for what. It also encourages being proactive and specific. However, it’s a common thing these days that companies, departments and teams don’t have a clear vision and metrics that will help verify the results. It might be due to many factors like low awareness, lack of time to create an actionable plan with specified goals or just insufficient knowledge how to do it.
So how can Product Design Sprint help you fight mentioned obstacles and create such a vision? The workshop aims at giving you a better understanding of your company, stakeholders, product and the environment. You execute numerous exercises that will help you discover the direction your company should be heading.
For example, the Customer Journey, one of the methodologies we use during PDS, ultimately leads you to a shared vision for product’s value proposition. Step by step, you discover who your target audience is, specify their needs and learn their behaviour. With such a roadmap you will have a more transparent look into the future and direction where your company should be going.
On the other hand, PDS is a good chance to discover the best framework for your business to create a vision and common goals to pursue. At Netguru we embraced V2MOM as the most suitable methodology. The idea behind V2MOM was conceptualised by the founders of SalesForce. V2MOM stands for Vision, Values, Methods, Obstacles and Metrics. In short, as Marc Benioff puts it:
The vision helped us define what we wanted to do. The values established what was most important about that vision; it set the principles and beliefs that guided it (in priority). The methods illustrated how we would get the job done by outlining the actions and the steps that everyone needed to take. The obstacles identified the challenges, problems, and issues we would have to overcome to achieve our vision. Finally, the measures specified the actual result we aimed to achieve; often this was defined as a numerical outcome.
Overcome stagnation and bring new improvements
The best companies on the market are flexible and agile in their actions. Flexible means that you have to keep in mind how you can develop your business no matter if it’s sales, strategy or people. If you’re standing still, you’re going backwards. In an agile approach, solutions evolve through team collaboration and adaptation to changes.
Product Design Sprint can be effective in moving your company forward. It enables verifying what’s working and what’s not by analysing the processes and possible ways to improve them. Whether it concerns technology, management or excessive bureaucracy, you can streamline the workflows to make them more efficient.

Build software that will meet your needs
Imagine software that generates a lot of costs and anxiety in your team. It’s important to determine their most crucial needs and what kind of software or workflow will help them to stay efficient. It’s essential to encourage yourself and others to bring about consistent improvements. For some of these issues you can simply schedule the brainstorming session or use some of the exercises from PDS to spark more creativity and engagement in the process.
In this area, we leveraged Value Proposition, another Product Design Sprint exercise. Together with Netguru Business Development Team, we identified some key pain points in their department. The major issue concerned repetitiveness of some tasks that were necessary to do, but very time-consuming. In the brainstorming session, we came up with some solutions to automate them. We introduced A/B tests in emails and a tool to hierarchise clients in terms of engagement they need. Not only did we improve methods and metrics to track different stats, but we also boosted customer satisfaction and their engagement.
Minimize bureaucracy
When scaling a business, processes scale up too. It leads to undesirable side effects like complex bureaucracy. It might be an issue with simplifying a contract process that takes many variables into consideration or building trust in order to manage important contract terms. To meet these needs, the team needs to understand users’ journeys throughout the entire purchase process.
From our perspective, cooperation with clients is not always as smooth as one could expect. Lack of information, non-effective communication plus mixed feelings on the part of our clients encouraged us to work on our processes. We’ve conducted PDS to find the missing points, gain our clients’ perspective and create a room for improvement. It also gave us the solid base for further discussion. When you don’t have a clear understanding of the problems at hand, it’s hard to find a meaningful solution.
Empower collaboration and communication
Most of us can agree with the statement that the biggest difficulty in companies is a lack of collaboration between departments. It’s often reflected by lack of efficiency in communication, miles long emails and threads, misunderstandings and lack of transparency. With over 600 people onboard, it’s getting increasingly harder. That’s why we had to redefine some processes, which involved more than one department.
Strictly speaking, we conducted another PDS exercise in which we tried to discover the biggest issues in communication between different teams. We collected feedback from distinct departments to detect areas which could be considered for improvement. It turned out that there was much potential to dwell on.
Product Design and RnD Teams succeeded in developing great products, but they struggled to promote them in an efficient way. With the help of a Marketing Department, they successfully released fully working products and concepts for applications such as: Callio, Ember Socket Guru, GitItBack, CarLens, atStats, and Pockee three of which were featured on Product Hunt. An IKEA online assistant concept was the fruit of Product Design and Marketing teams’ cooperation. As a result, it was featured on Behance and widely recognised by international press and design communities. It’s been all achieved thanks to regular meetings, common processes and communication channels we introduced.
What does the client get after the workshop?
At the end of the sprint, the client gets a better understanding of their users’ problems and multiple ideas on how to solve them. We prepare a detailed report on the workshop with all materials and canvases digitized. The report also contains suggestions about which way the product should go. Additionally, the clients usually get a working lo-fi prototype for some of our user stories, which they can test later.
If a client decides to build a product with us they'll also get:
- a project roadmap, broken down into phases
- pre-defined tasks for each phase ready for developers to start their work.
Summary
Building great ideas into elegant, thoughtful, engaging solutions is hard. Even harder when you and your customers are not included in the creation of those solutions. Especially for larger organisations. With faster, better solutions that your customers are using and promoting, there comes a better overall health of your business.
As you can see, there is a lot of value in implementing Product Design Sprint. It’s not the ultimate solution for everything, but it definitely inspires to take action.The complex or inefficient processes became much easier to solve. We tested it many times with our clients and after each session a variety of conclusions and things to improve came out. If you want to give PDS a shot in your business, drop us a message and schedule a Product Design Sprint session with Netguru.







